title: Algorithm_Sort
tags:
- Technology
- Algorithm
date: 2022-04-13 13:18#
Algorithm_Sort#
Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, return an array of the squares of each number sorted in non-decreasing order.
QuickSort#
Implementation logic:
Take the value at the specified index key, compare it with the numbers before the index, and if the number before is greater than the number after, swap positions.
For example:
[ 8 3 5 1 4 2 ]
Starting from index 1, the current element is 3, and the previous element is 8. Since 8 > 3, swap positions. The array becomes [ 3 8 5 1 4 2 ].
Then, at index 2, the current element is 5, and the previous element is 8. Since 8 > 5, swap positions. The array becomes [ 3 5 8 1 4 2 ].
Then, at index 3, the current element is 1, and the previous element is 8. Since 8 > 1, swap positions. The array becomes [ 3 5 1 8 4 2 ]. Since 5 > 1, swap positions. The array becomes [ 3 1 5 8 4 2 ]. Since 3 > 1, swap positions. The array becomes [ 1 3 5 8 4 2 ].
Then, at index 4, the current element is 4, and the previous element is 8. Since 8 > 4, swap positions. The array becomes [ 1 3 5 4 8 2 ]. Since 5 > 4, swap positions. The array becomes [ 1 3 4 5 8 2 ].
Then, at index 5, the current element is 2, and the previous element is 8. Since 8 > 2, swap positions. The array becomes [ 1 3 4 5 2 8 ]. Since 5 > 2, swap positions. The array becomes [ 1 3 4 2 5 8 ]. Since 4 > 2, swap positions. The array becomes [ 1 3 2 4 5 8 ]. Since 3 > 2, swap positions. The array becomes [ 1 2 3 4 5 8 ]. Since 1 < 2, stop.
The code is as follows:
class Solution {
func sortedSquares(_ nums: [Int]) -> [Int] {
// first, get the squareList
var squareNums = nums.map({ $0 * $0 })
for j in 0..<squareNums.count {
let key = squareNums[j]
var i = j - 1
while (i >= 0 && squareNums[i] > key) {
squareNums[i+1] = squareNums[i]
i = i - 1
}
squareNums[i+1] = key
}
return squareNums
}
}
Selection Sort#
Implementation logic:
Traverse the array to find the smallest value and place it at index 0 of the result array.
Traverse the array to find the second smallest value and place it at index 1 of the result array.
...
The code is as follows:
class Solution {
func sortedSquares(_ nums: [Int]) -> [Int] {
// first, get the squareList
var squareNums = nums.map({ $0 * $0 })
// selectionSort
let count = squareNums.count
for i in 0..<(count-1) {
var j_min = i
var j = i+1
// Traverse to find the index of the smallest element starting from i
while (j < count) {
if squareNums[j] < squareNums[j_min] {
j_min = j
}
j = j + 1
}
// If i and the index of the smallest element are not equal, swap the elements at the two positions
if i != j_min {
squareNums.swapAt(i, j_min)
}
}
return squareNums
}
}
Bubble Sort#
Logic:
Iterate through adjacent pairs of elements. If the previous element is greater, swap positions. Continue comparing the next pair of elements.
Repeat the above steps.
Repeat the above steps.
...
Continue until there are no elements left to swap positions.
For example:
[2, 1, 6, 4, 7, 5]
First iteration:
index = 1; current element is 2, previous element is 1, 2 < 1, swap positions, [1, 2, 6, 4, 7, 5]
index = 2; current element is 6, previous element is 2, 6 > 2, no need to swap positions
index = 3; current element is 4, previous element is 6, 4 < 6, swap positions, [1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 5]
index = 4; current element is 7, previous element is 6, 7 > 6, no need to swap positions
index = 5; current element is 5, previous element is 7, 5 < 7, swap positions, [1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7]
There was a swap in the middle.
Second iteration:
index = 1; current element is 2, previous element is 1, 2 > 1, no need to swap positions, [1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7]
index = 2; current element is 4, previous element is 2, 4 > 2, no need to swap positions
index = 3; current element is 6, previous element is 4, 6 > 4, no need to swap positions
index = 4; current element is 5, previous element is 6, 5 < 6, swap positions, [1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7]
index = 5; current element is 7, previous element is 6, 7 > 6, no need to swap positions
There was a swap in the middle.
Third iteration:
index = 1; current element is 2, previous element is 1, 2 > 1, no need to swap positions, [1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7]
index = 2; current element is 4, previous element is 2, 4 > 2, no need to swap positions
index = 3; current element is 6, previous element is 4, 6 > 4, no need to swap positions
index = 4; current element is 6, previous element is 5, 6 > 5, no need to swap positions
index = 5; current element is 7, previous element is 6, 7 > 6, no need to swap positions
No swaps were made in this iteration, so the iteration ends.
The code is as follows:
class Solution {
func sortedSquares(_ nums: [Int]) -> [Int] {
// first, get the squareList
var squareNums = nums.map({ $0 * $0 })
// bubble sort
var sorted = false;
while (!sorted) {
sorted = true
for i in 1..<(squareNums.count) {
if (squareNums[i] < squareNums[i-1]) {
squareNums.swapAt(i, i-1)
sorted = false
}
}
}
return squareNums
}
}
Merge Sort#
Implementation logic:
Split the array into two halves, then continue splitting the two halves until the number of elements in the array is 1. Then compare and return the sorted smallest array, and then sort, merge, and concatenate.
The diagram below shows the process:
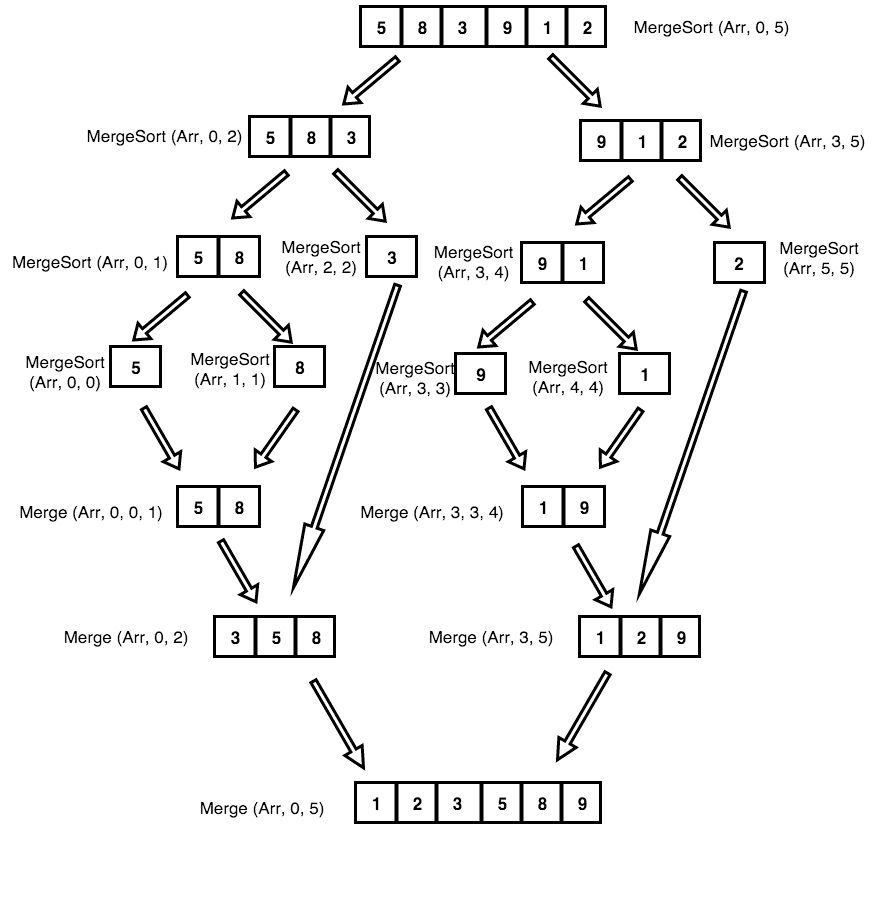
The code is as follows:
class Solution {
func merge(_ left: [Int], _ right: [Int]) -> [Int] {
// Define a new array to store the sorted result
var result: [Int] = []
// Make the input parameters mutable
var mutLeft = left
var mutRight = right
// Sort by traversing
while mutLeft.count > 0 && mutRight.count > 0 {
// Sort
// If the left side is smaller, remove the first element from the left side and add it to the result array; otherwise, remove the first element from the right side and add it to the result array.
result.append(mutLeft[0] < mutRight[0] ? mutLeft.removeFirst() : mutRight.removeFirst())
}
// Concatenate the non-empty array
result += (mutLeft.count > 0 ? mutLeft : mutRight)
// Return
return result
}
func mergeSort(_ nums: [Int]) -> [Int] {
// If the number of array elements is less than 2, no further splitting is required, so return the array
if nums.count < 2 {
return nums
}
// Split the array in half
let middle = nums.count / 2
// Take the first half from 0 to middle (excluding middle)
let leftSlice = nums[0..<middle]
// Continue splitting
let subLeft = mergeSort(Array(leftSlice))
// Take the second half from middle to the end
let rightSlice = nums[middle..<nums.count]
// Continue splitting
let subRight = mergeSort(Array(rightSlice))
// After splitting to the smallest unit, sort, merge, and return
return merge(subLeft, subRight)
}
func sortedSquares(_ nums: [Int]) -> [Int] {
// first, get the squareList
var squareNums = nums.map({ $0 * $0 })
// merge sort
return mergeSort(squareNums)
}
}